Accessible Names and Descriptions
ARIA brings with it a foundational concept for all HTML markup: accessible names and descriptions.
The text content or value exposed from a default button, link, form input, or even a heading is referred to as an “accessible name”.
Text exposed on an element with a title attribute is called an “accessible description.” Descriptions are announced in a screen reader after a bit of a delay and can be configured on or off (so don’t count on them being announced). Descriptions can also fill in as accessible names when there is no accessible name otherwise.
Both types of content are important in Assistive Technology: what is that element even for? The accessible name or description should give users that information.
Aria-label, aria-labelledby, & aria-describedby
You can also bolt on both accessible names and descriptions using explicit ARIA attributes like aria-label, aria-labelledby, and aria-describedby!
You can put a string value in aria-label on an element with a qualifying role, like a <button> or a landmark element. Example:
<button aria-label="Settings"></button>Both aria-labelledby and aria-describedby take an ID as a value that matches another element: handy for reusing content already on the page.
<section aria-labelledby="section-heading-2">
<h2 id="section-heading-2">All About Wombats</h2>
</section>Say you have multiple pieces of content on an element: text content, an aria-label, maybe even an aria-labelledby and an aria-describedby. Which one wins? Something has to be announced first in a predictable way cross-platform, or accessible naming would be absolute chaos.
That’s where ARIA and related specs are so valuable. They detail the order that content should be exposed for accessible naming, which doesn’t rely on source order (i.e. start-to-end in the markup). One attribute may very well cancel out another, according to the standard algorithm.
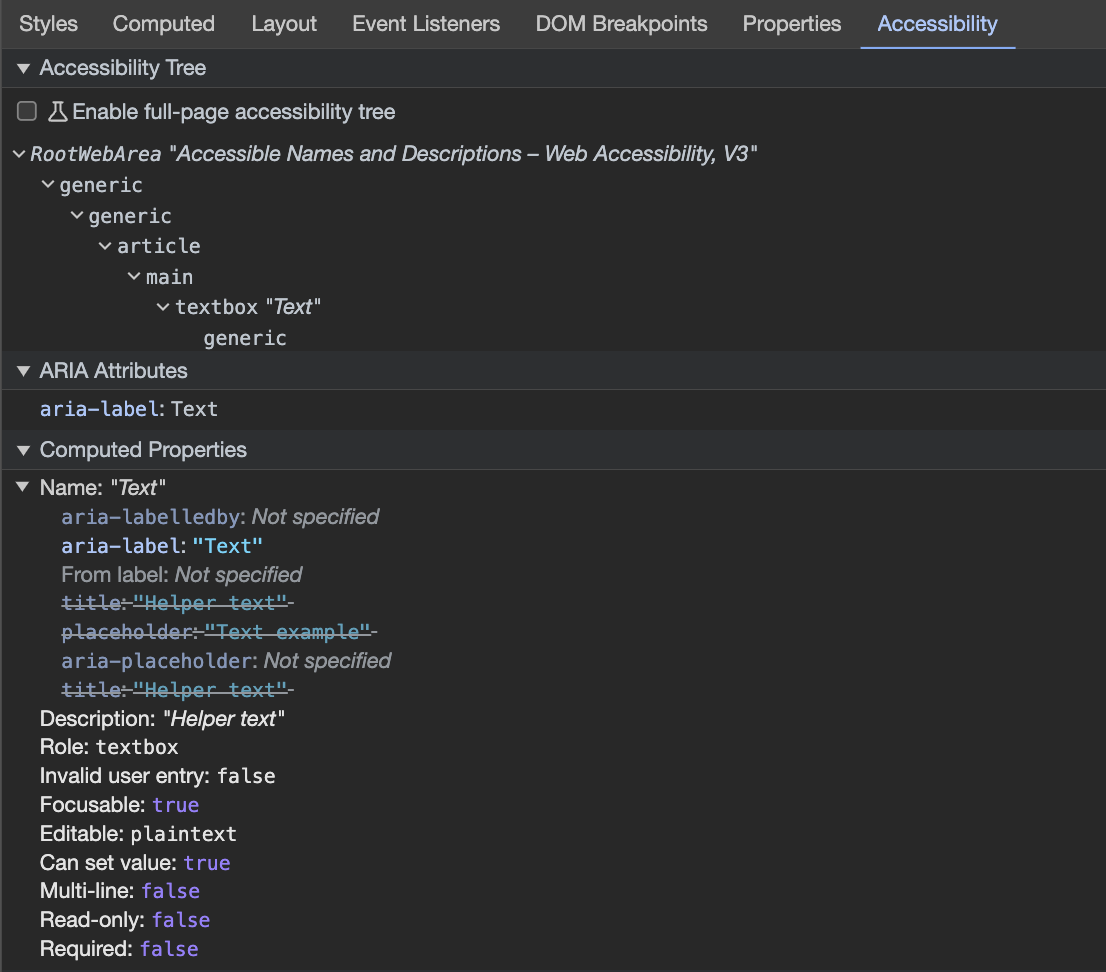
DevTools for labeling
A tool I’d highly recommend to verify your accessible names and labels is the Chrome Accessibility Inspector in DevTools. In the Elements panel next to Styles, Computed, etc., all the way at the end is an Accessibility tab. It will show you which naming attribute “wins” and save you some headaches with lightweight testing.